Data Warehouse Fundamentals :
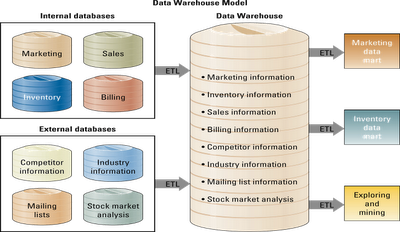
Data warehouse - a logical collection of information, gathered from many different operational databases that supports business analysis activities and decision making tasks.
Data warehouse - a logical collection of information, gathered from many different operational databases that supports business analysis activities and decision making tasks.
Primary purpose of a data warehouse is to aggregate information throughout an organization into a single repository decision-making purposes.
Extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) - a process that extracts information from internal and external databases, transform the information using a common set of enterprise definitions, and loads the information into a data warehouse.
Data mart - contains a subset of data warehouse information.
Multidimensional Analysis and Data Mining :
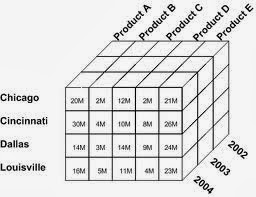
Cube - common term for the representation of multidimensional information.
Data Mining - the process of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone.
Data Mining Tool - uses a variety of techniques to find patterns and relationships in large volumes of information and infers rules that predict future behaviour and guide decision making.
Information Cleansing or Scrubbing :
Is a process that weeds out and fixes or discards inconsistent, incorrect, or incomplete information.
Business Intelligence :
Information that people use to support their decision making efforts.

Multidimensional Analysis and Data Mining :
Cube - common term for the representation of multidimensional information.

Data Mining - the process of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone.
Data Mining Tool - uses a variety of techniques to find patterns and relationships in large volumes of information and infers rules that predict future behaviour and guide decision making.
Information Cleansing or Scrubbing :
Is a process that weeds out and fixes or discards inconsistent, incorrect, or incomplete information.
Business Intelligence :
Information that people use to support their decision making efforts.
Principle BI enablers includes technology, people and culture.

.jpg)
